
团结 自强 敬业 创新
遵义医科大学附属医院.公益
The role of microglia in Alzheimer's disease and progress of treatment
小胶质细胞在阿尔茨海默病中的作用和治疗进展
Yi-Huan Guan, Ling-Jing Zhang, Shi-Ya Wang, Ya-Dan Deng, Hong-Su Zhou, Dong-Qing Chen, Lan-Chun Zhang
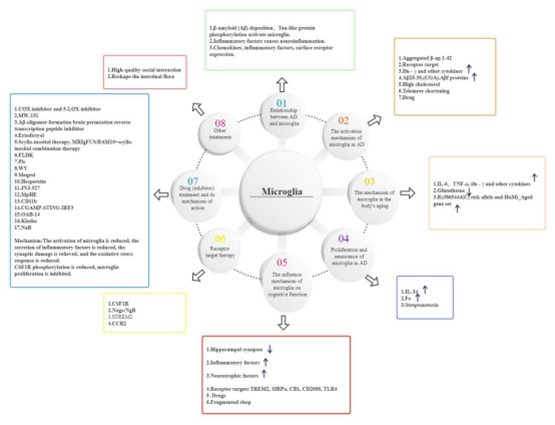
Microglia are permanent immune cells of the central nervous system. Microglia play an important role in the pathological process of Alzheimer's disease (AD). They are mainly involved in the uptake and clearance of amyloid-β (Aβ), as well as development of neuroinflammation. We found that overactivated microglia induce an increase in Aβ and Tau, and Aβ and Tau in turn act as activators of microglia. Additionally, various cytokines and proteins, high cholesterol, and telomere shortening are all associated with microglia activation. More activated microglia induce the release of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors to regulate inflammation, while microglia express multiple homologous receptors that bind to neuroimmunomodulators to prevent microglia overactivation. Moreover, aging of the body promotes neuroinflammation by increasing the response to IFN-γ (interferon-γ), and aging of the microglia themselves promotes AD by inducing the accumulation of large amounts of iron and reducing autophagy by regulating protein levels. Cognitive dysfunction occurs when activated microglia induce an increase in beta oligomers, promoting the production of pro-inflammatory factors that alter the shape, composition, and density of synapses. Based on their correlation, microglia-mediated AD therapy as well as the corresponding targets and drugs are discussed. In contrast to similar reviews, this article also summarizes some novel microglia-mediated AD treatment methods over the recent years.
小胶质细胞是中枢神经系统的永久免疫细胞。小胶质细胞在阿尔茨海默病(AD)的病理过程中起着重要作用。它们主要参与淀粉样蛋白-β(Aβ)的摄取和清除,以及神经炎症的发展。我们发现过度激活的小胶质细胞诱导Aβ和Tau的增加,而Aβ和Tau反过来充当小胶质细胞的激活剂。此外,各种细胞因子和蛋白质、高胆固醇和端粒缩短都与小胶质细胞活化有关。更多活化的小胶质细胞诱导炎症和抗炎因子的释放以调节炎症,而小胶质细胞表达多种同源受体,这些受体与神经免疫调节剂结合以防止小胶质细胞过度激活。此外,身体的衰老通过增加对IFN-γ(干扰素-γ)的反应来促进神经炎症,而小胶质细胞本身的衰老通过诱导大量铁的积累并通过调节蛋白质水平减少自噬来促进AD。当活化的小胶质细胞诱导β-低聚物增加时,就会发生认知功能障碍,促进促炎因子的产生,从而改变突触的形状、组成和密度。基于它们的相关性,讨论了小胶质细胞介导的AD治疗以及相应的靶点和药物。与类似的综述相比,本文还总结了近年来一些新型的小胶质细胞介导的AD治疗方法。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12023
Stellate ganglion intervention for chronic pain: A review
星状神经节干预治疗慢性疼痛
Qing-Yang Luo, Song Wen, Xin-Ran Tan, Xi Yi, Song Cao
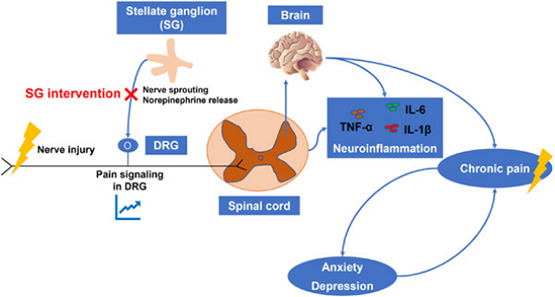
The possible mechanism of stellate ganglion intervention (SGI) may relieve chronic pain associated with sympathetic maintenance by inhibiting dorsal root ganglion (DRG) nerve sprouting, norepinephrine release, and pain signaling generation in the DRG. Besides, SGI can relieve chronic pain, anxiety, and depression by inhibiting neuroinflammation in the spinal cord and in the brain.
星状神经节干预(SGI)的可能机制可以通过抑制DRG中背根神经节(DRG)神经萌发、去甲肾上腺素释放和疼痛信号生成来缓解与交感神经维持相关的慢性疼痛。此外,SGI可以通过抑制脊髓和大脑中的神经炎症来缓解慢性疼痛,焦虑和抑郁。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12047
Update on neurological symptoms in patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2
关于严重急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒-2感染患者的神经系统症状的最新研究
Mei-Fang Xiao, Zhi-Jian You, Chang Zeng, Ze-Bing Huang, Liang Dong
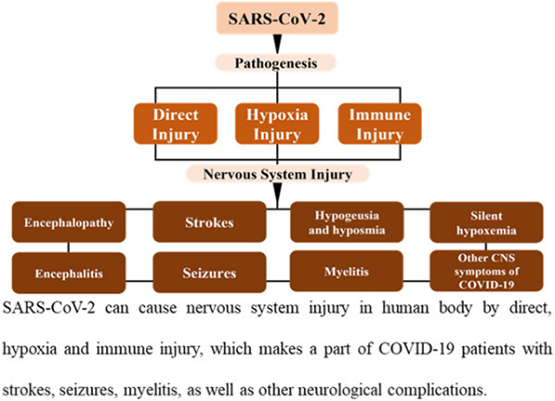
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 can cause nervous system injury in the human body by direct, hypoxia, and immune injury, which affects a part of novel coronavirus 19 patients with strokes, seizures, myelitis, as well as other neurological complications.
重症急性呼吸综合征冠状病毒-2可通过缺氧和免疫损伤直接引起人体神经系统损伤,在部分新型冠状病毒患者出现脑卒中、癫痫发作、脊髓炎以及其他神经系统并发症。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12008
Effects of norepinephrine on microglial neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain
去甲肾上腺素对小胶质细胞神经炎症和神经性疼痛的影响
He-Lin Zou, Juan Li, Jun-Li Zhou, Xi Yi, Song Cao
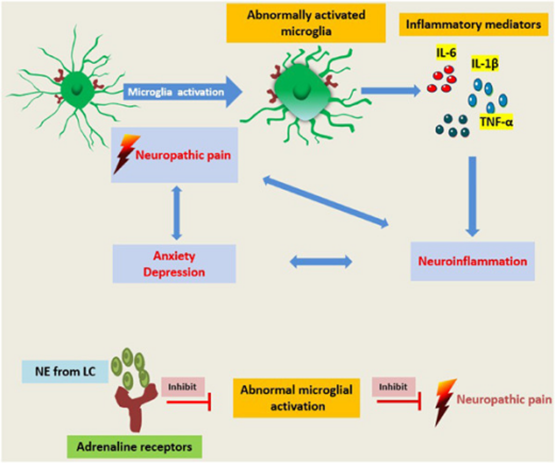
Abnormally activated microglia release inflammatory mediators and cause neuroinflammation. Persistent neuroinflammation may cause anxiety/depression. Neuropathic pain and neuroinflammation affect each other to form a vicious circle. Norepinephrine released from the locus coeruleus inhibits abnormal microglial activation and relieves chronic pain.
异常活化的小胶质细胞释放炎症介质并引起神经炎症。持续的神经炎症可能导致焦虑/抑郁。神经性疼痛和神经炎症相互影响,形成恶性循环。从腔规则位点释放的去甲肾上腺素抑制异常小胶质细胞激活并缓解慢性疼痛。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12001
Potential natural products for the management of autism spectrum disorder
用于治疗自闭症谱系障碍的潜在天然产品
Punya Sachdeva, Intizaar Mehdi, Rohit Kaith, Faizan Ahmad, Md Sheeraz Anwar
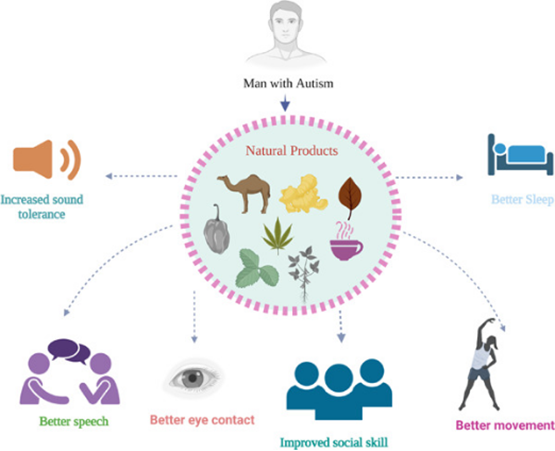
The figure explains that improvement like increased sound tolerance, better sleep pattern, better speech, improved social skills, and better eye contact and movement has been seen in patients with autism. An improvement in the symptoms can be observed by treating with natural products, such as camel's milk, luteolin, green tea, piperine, curcumin, cannabinoids, Ginkgo biloba, and Bacopa monnieri.
该图解释了在自闭症患者中观察到的改善,如增加声音耐受力、更好的睡眠模式、更好的言语、改善的社交技能以及更好的眼神交流和运动。通过使用天然产品,如骆驼奶、木犀草素、绿茶、胡椒碱、姜黄素、大麻素、银杏和巴科帕可观察到症状改善。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12050
Research advances in the clinical application of esketamine
艾氯胺酮临床应用研究进展
Xiao-Xi Zhang, Nai-Xin Zhang, De-Xing Liu, Jun Ding, Yi-Nan Zhang, Zhao-Qiong Zhu
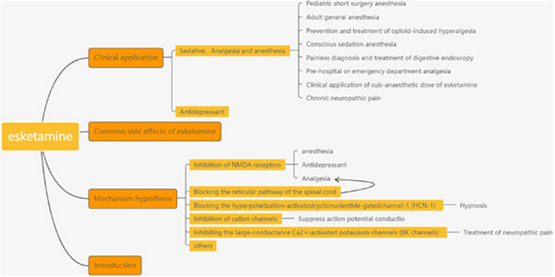
This article describes esketamine from four aspects, namely the mechanism, common clinical applications, common side effects, and prospects for esketamine. It describes the advantages of esketamine at the current stage, its unique role in some special fields, and compares it with ketamine.
本文从艾氯胺酮的机制、常见临床应用、常见副作用、展望四个方面对艾氯胺酮进行介绍。介绍了现阶段艾氯胺酮的优势,在一些特殊领域的独特作用,并与氯胺酮进行了比较。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12019
Effect of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block combined with acupuncture in the treatment of nervous tinnitus and earache: a case report
超声引导下星状神经节阻滞联合针灸治疗神经性耳痛的病例报告
Song Wen, Min-Fu You, Liu-Lin Xiong, Qiao Hu, En Liu
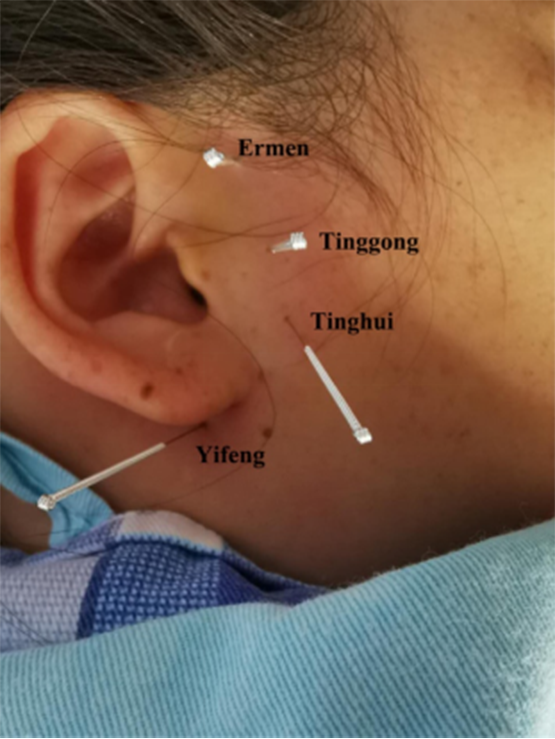
Nervous tinnitus is one of the most common hearing impairments, which seriously affects the physical and mental health of patients. We describe a case of a 31-year-old female with nervous tinnitus in this report. She suffered from bilateral tinnitus for more than 8 months with the symptoms of earache, anxiety, and sleep disorders at admission. Under the combined treatment of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block and acupuncture at acupoints of the Ermen, Tinggong, Tinghui, and Yifeng, the patient recovered well and the symptoms such as tinnitus and earache disappeared gradually. This case may provide a reference for the subsequent clinical treatment of tinnitus.
神经性耳鸣是最常见的听力障碍之一,严重影响患者的身心健康。我们在这份报告中描述了一个31岁女性神经性耳鸣的病例。她患有双侧耳鸣8个多月,入院时出现耳痛、焦虑和睡眠障碍症状。在二门、廷功、庭辉、宜丰穴位超声引导下星状神经节阻滞和针灸联合治疗下,患者恢复良好,耳鸣、耳痛等症状逐渐消失。本病例可为耳鸣后续临床治疗提供参考。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2769-2795.2020.tb00056.x
Effects of different injection methods of propofol anesthesia on the behavior and electroencephalography recording in mice
异丙酚麻醉不同注射方式对小鼠行为及脑电图记录的影响
Dan Luo, Shi-Yu Chen, Yu Zhang
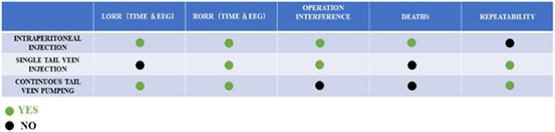
Intraperitoneal injection of propofol can collect the time and electroencephalography (EEG) of loss of righting reflex (LORR) and RORR, but it has operational interference, high mortality, and poor repeatability. Single tail vein injection of propofol has high repeatability and low mortality, but only the time and EEG of RORR can be collected, and there is operational interference in the experiment. Continuous tail vein pumping of propofol can collect the time and EEG of LORR and RORR, with no operational interference, low mortality, and high repeatability in the experiment.
腹腔注射丙泊酚可采集矫正反射丧失(LORR)和RORR的时间和脑电图(EEG),但具有操作干扰,死亡率高,重复性差。异丙酚单尾静脉注射重复性高,死亡率低,但只能采集RORR的时间和脑电图,实验中存在操作干扰。异丙酚连续尾静脉泵送可采集LORR和RORR的时间和脑电图,实验无操作干扰,死亡率低,重复性高。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12030
The role of intracerebral dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in sleep-wake cycles and general anesthesia
脑内多巴胺D1和D2受体在睡眠-觉醒周期和全身麻醉中的作用
Jie Zhang, Jia Li, Cheng-Xi Liu, Huan Gui, Cheng-Dong Yuan, Yi Zhang
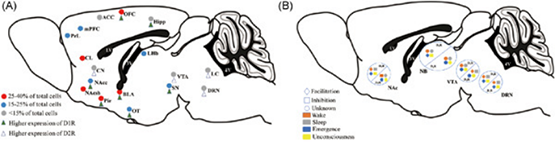
The distribution of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the central nervous system is shown here. Activation of D1R in NAc, DRN, and NB promotes awakening from natural sleep and general anesthesia. D2R acts in a brain area-dependent manner, with D2R in NAc playing a sleep-promoting role and D2R in DRN and ventral tegmental area a awakening-promoting role, and the function of both receptors in other brain areas remains to be further investigated.
多巴胺D1和D2受体在中枢神经系统中的分布如图所示。NAc、DRN 和 NB 中 D1R 的激活可促进从自然睡眠和全身麻醉中醒来。D2R以大脑区域依赖的方式起作用,NAc中的D2R起促进睡眠的作用,DRN和腹侧被盖区的D2R起着觉醒促进作用,两种受体在其他大脑区域的功能仍有待进一步研究。
全文链接: https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12024
关于Ibrain

Ibrain 是科研和教育领域的全球领导者——Wiley公司出版发行的、由遵义医科大学附属医院主办的神经科学领域的英文开放获取期刊。该期刊出版关于脑、脊髓和神经的前沿研究,为神经科学家提供基础和转化医学以及临床实践的交流平台。Ibrain 主编由四川大学华西医院神经疾病研究室主任王廷华教授和南澳大利亚大学Xin-Fu Zhou教授担任。
期刊发表范围和主题:
Ibrain 对脑、脊髓和神经疾病相关的主题感兴趣,包括但不限于临床医学、分子诊断、表观遗传学/遗传学、细胞生物学、药物发现、进化医学、纳米技术和人工智能。该期刊聚焦临床和实验研究进展,为脑、脊髓和神经疾病提供表征、致病机制、诊断、治疗、医疗创新和技术。
期刊发表的主题包括但不限于:
期刊发表文章类型:
Original article
Reviews
Comments
Case reports
Letter
Methods
2022-2024年期刊免收论文出版费(APC)。
目前Ibrain 被国际检索数据库DOAJ收录,从提交申请到被DOAJ收录仅用两个月的时间。竭诚欢迎神经科学领域的科研工作者、医生、研究生积极向期刊投稿!
投稿链接:
https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/ibra
特刊征稿
Ibrain 将出版两期特刊:
特刊一发表CNS损伤注射材料的最新基础和临床研究。它将聚焦应用注射材料修复脑损伤的分子机制研究、有效注射材料的基础和临床研究以及相关主题。
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/27692795/themed-collections/injectable_materials
特刊二提供神经变性、神经痛和神经病理性疼痛的最新基础和临床研究。重点介绍神经退行性变、神经痛和神经病理性疼痛的分子机制研究、基础和临床研究以及相关主题。
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/page/journal/27692795/themed-collections/neurodegeneration
我们诚挚邀请研究人员为特刊提供原创研究论文或综述文章。
遵义医科大学附属医院党委宣传部
审核:勾强
编辑:肖毅
修改:张洁